ADOK Desenvolvimento de Sistemas presents
JAVA Programmer's Brain ScreenSaver
100% Freeware!!!
|
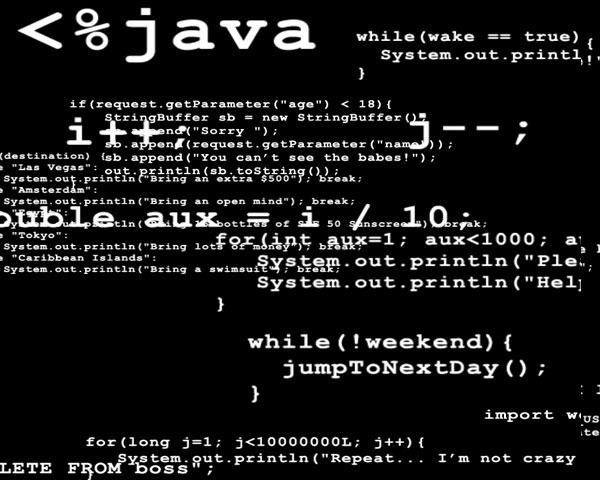
Java is a programming language originally developed by Sun Microsystems and released in 1995. Java applications are typically compiled to bytecode, although compilation to native machine code is also possible. At runtime, bytecode is usually either interpreted or compiled to native code for execution, although direct hardware execution of bytecode by a Java processor is also possible. Java Programmer's Brain ScreenSaver show in the screen lot of funny codes in Java simulating one crazy programmer's brain. 100% Freeware - Spyware free, virus free, malware free. |
| What's Java? Java is a programming language originally developed by Sun Microsystems and released in 1995. Java applications are typically compiled to bytecode, although compilation to native machine code is also possible. At runtime, bytecode is usually either interpreted or compiled to native code for execution, although direct hardware execution of bytecode by a Java processor is also possible. The language derives much of its syntax from C and C++ but has a simpler object model and fewer low-level facilities. JavaScript, a scripting language, shares a similar name and has similar syntax, but is not directly related to Java. The original and reference implementation Java compilers, virtual machines, and class libraries were developed by Sun from 1995. As of May 2007, in compliance with the specifications of the Java Community Process, Sun made available most of their Java technologies as free software under the GNU General Public License. Others have also developed alternative implementations of these Sun technologies, such as the GNU Compiler for Java and GNU Classpath. |
| Wikipedia Definition Original URL: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Java_(programming_language) Java started as a project called "Oak" (The name came from an oak tree that stood outside the Sun Microsystems office) by James Gosling in June 1991 for use in a set top box project.[3] Gosling's goals were to implement a virtual machine and a language that had a familiar C/C++ style of notation[4]. The first public implementation was Java 1.0 in 1995. It promised "Write Once, Run Anywhere" (WORA), providing no-cost runtimes on popular platforms. It was fairly secure and its security was configurable, allowing network and file access to be restricted. Major web browsers soon incorporated the ability to run secure Java "applets" within web pages. Java became popular quickly. With the advent of "Java 2", new versions had multiple configurations built for different types of platforms. For example, J2EE was for enterprise applications and the greatly stripped down version J2ME was for mobile applications. J2SE was the designation for the Standard Edition. In 2006, for marketing purposes, new "J2" versions were renamed Java EE, Java ME, and Java SE, respectively. In 1997,Sun Microsystems approached the ISO/IEC JTC1 standards body and later the Ecma International to formalize Java, but it soon withdrew from the process.[5][6][7] Java remains a de facto standard that is controlled through the Java Community Process.[8] Sun used to make most of its Java implementations available without charge though they were closed-source, proprietary software. Sun's revenue from Java was generated by the selling of licenses for specialized products such as the Java Enterprise System. Sun distinguishes between its Software Development Kit (SDK) and Runtime Environment (JRE) which is a subset of the SDK, the primary distinction being that in the JRE, the compiler, utility programs, and many necessary header files are not present. On 13 November 2006, Sun released much of Java as free software under the terms of the GNU General Public License (GPL). On 8 May 2007 Sun finished the process, making all of Java's core code open source, aside from a small portion of code to which Sun did not hold the copyright.[9] Primary goals - It should use the object-oriented programming methodology.
|